What is the significance of this?
- Using this repository, you can provision the application as well as all of your cloud infrastructure with a single command.
How is automation accomplished?
- Terraform has been used to provision infrastructure on AWS.
- To make provision for application On the AWS EKS, deployment has been performed through using Helm template.
- To fit the Kubernetes design, the NodeJS service has been changed to a microservice.
- Terraform has been converted into a docker container microservice to improve team cooperation by ensuring that everyone uses the same version of the software.
- This project makes use of Makefile to automate the provisioning of the full stack with a single command.
- For convenience of usage, the load and performance testing tool locust has been transformed into a docker container.
Prerequisite
- AWS account access
- AWS iam programmatic user access with the follwing policy attached to the user
- AmazonEC2FullAccess,IAMFullAccess,AutoScalingFullAccess,AmazonEKSClusterPolicy, 
- AmazonEKSWorkerNodePolicy,AmazonVPCFullAccess,AmazonEKSServicePolicy,AmazonEKS_CNI_Policy
Source Code
https://github.com/Lforlinux/aws-terraform-nodejs
How to provision the infra
Makefile has been leveraged for the simple approach towards the one-click entire stack deployment.
- GIT Clone this repo
- Configure your AWS credentials.
- Just deploy the entire stack by following single command.
make deploy
- Review the resources and type yes.
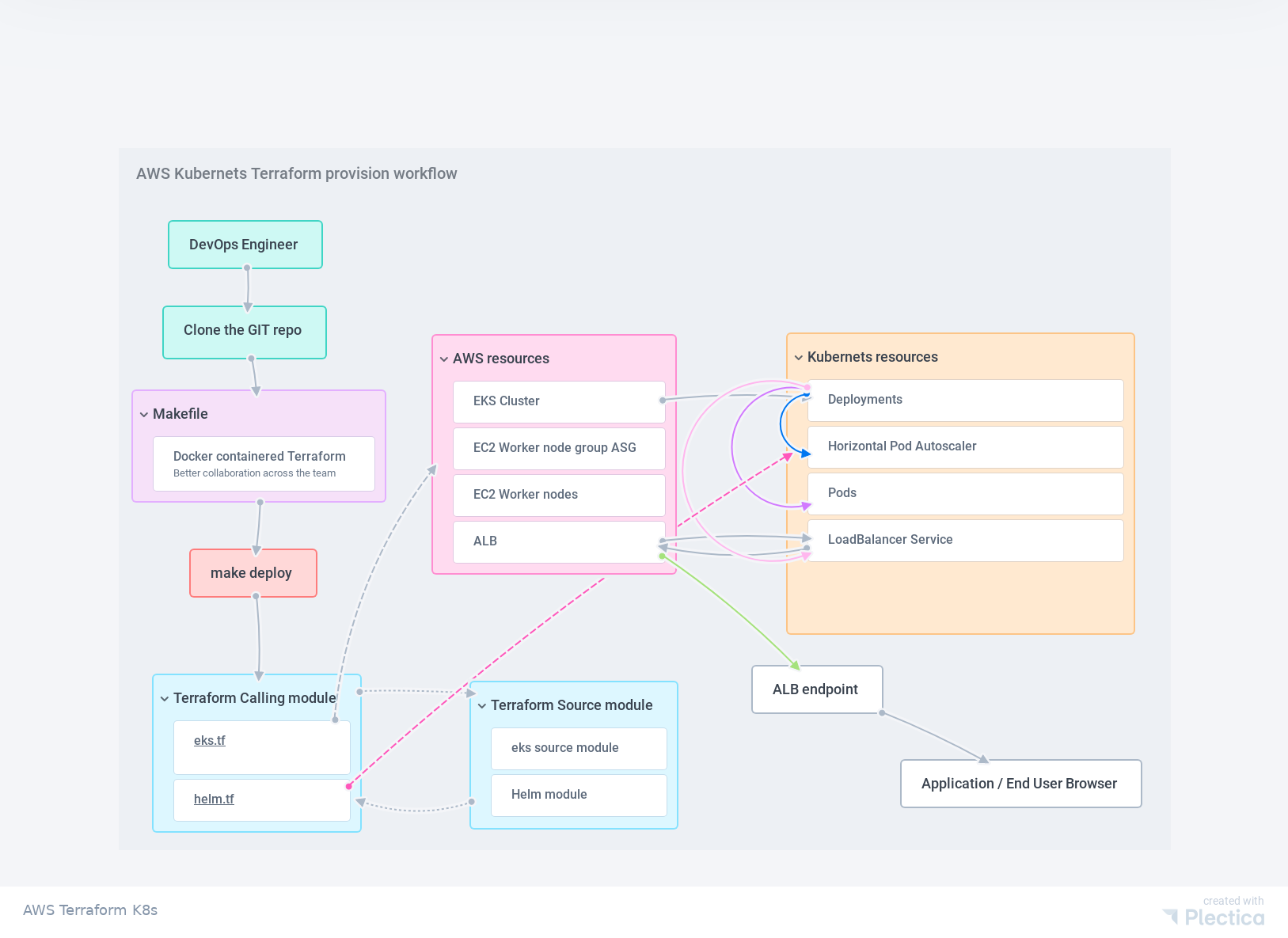
- Detailed workflow has been given on the following diagram.
Workflow diagram.
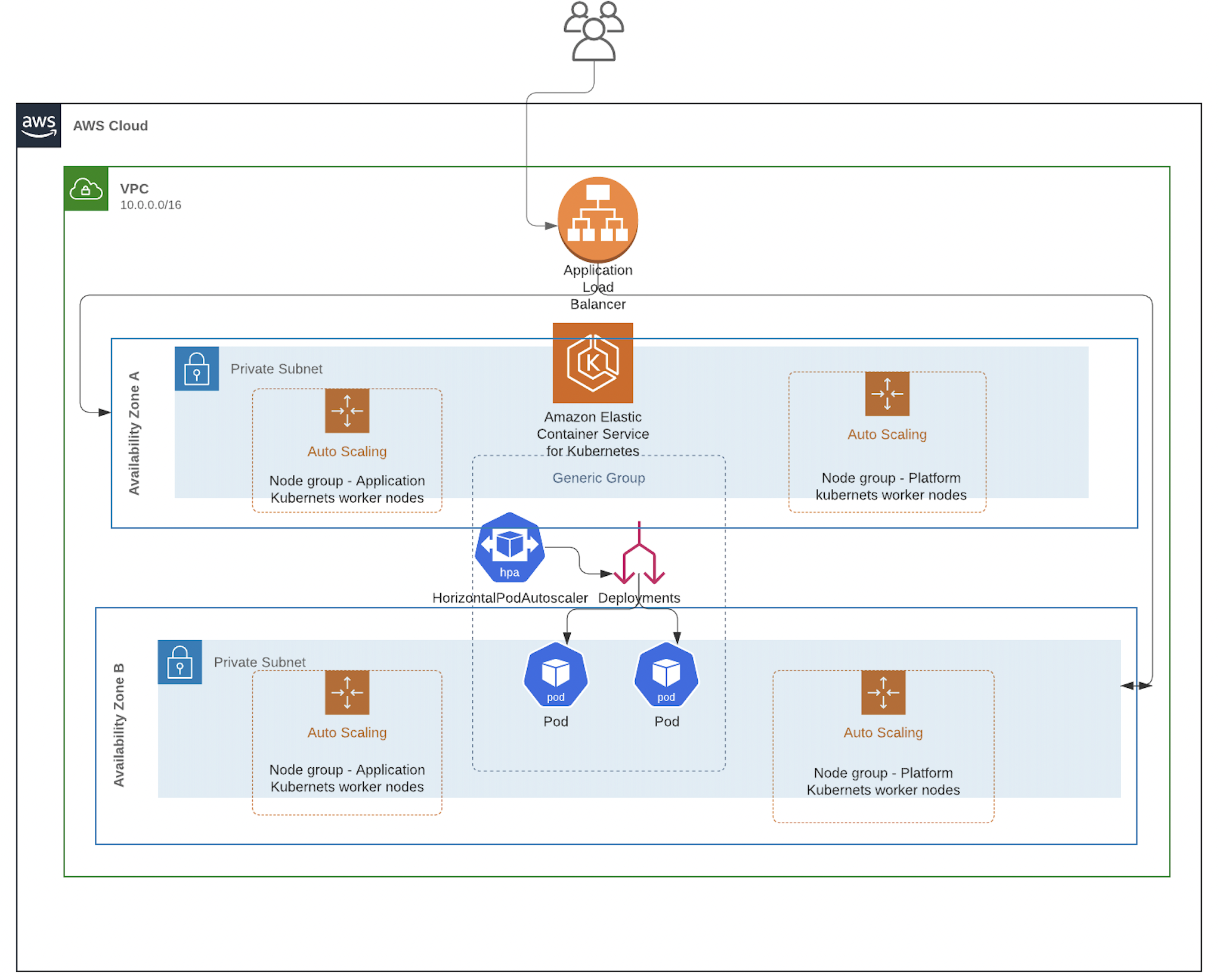
Architecture.
How to see the application and access the Kubernetes cluster.
- If you are running the
make deployinside laptop/ AWS instance. The Kubernetes kubeconfig will be posted on the same directory. You can make use of this kubeconfig if you are using any K8s tools like Lens or any other k8s IDE. - Another way to access the k8s cluster is via kubectl.
- set the context by the following command after
make deploy aws eks --region $(terraform output -raw region) update-kubeconfig --name $(terraform output -raw cluster_name)- Above command will set the context to use the kubectl.
- Now ALB URL will be available by
kubectl get svcor go to the AWS ALB console and copy and use it on any browser.
[ec2-user@ip-172-31-83-136 aws-terraform-nodejs]$ kubectl get svc
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
nodejsapplication-helm-nodejs LoadBalancer 172.20.83.16 a0a551a21584c449a961842a873b38c6-718686509.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com 80:31924/TCP 18m
- Port 80 for the NodeJS application is open on the internet.
How fault tolerance with high availability achieved
- K8s resources are deployed as deployment and mapped to Horizontal Pod Autoscaler.
- HPA will look after the pod’s memory and CPU utilization and it will increase the pods' count and decrease the pod count if the load pressure comes under control.
- K8s worker nodes are deployed are AWS Auto Scaling Group.
Performance Testing / Load Testing.
- use the following command to do performance/load testing.
# export TARGET_HOST=Place-your-ALB-URL-Here
# docker run -i --rm -v $PWD/reports:/opt/reports -v ~/.aws:/root/.aws -v $PWD/:/opt/script -v $PWD/credentials:/meta/credentials -p 8089:8089 -e ROLE=standalone -e TARGET_HOST=$TARGET_HOST -e LOCUST_FILE=https://raw.githubusercontent.com/zalando-incubator/docker-locust/master/example/simple.py -e SLAVE_MUL=4 -e AUTOMATIC=False registry.opensource.zalan.do/tip/docker-locust
- open your local browser and use localhost:8089 (The IP varies Depending on where you are running the above docker command)
- Give the user and load iteration above 1000 concurrent users to generate the load.
- Monitor the pod’s counts and HPA as per the load the pod’s count will be increased via HPA component.
Application lifecycle Management with zero downtime.
- Make sure to do the code change for the Nodejs app given on this same directory.
- Do docker build and push it to the Docker registry
- Once we have the latest image available create a branch from this repository
- append new image tag on the NodeJS helm chart values.yaml file.
- Create a PR
- Apply the change by running terraform
make deploy - Deployment will be performed by Helm. The K8s deployment will take care of rolling updates on the pods to achieve zero downtime.
Enhancement
- The whole orchestration can be performed via Jenkins as a scripted/Declatrative pipeline
- Helm chart can be packaged and placed in a separate registry which will give more leverage for our App lifecycle management.
- GitOps model can be implemented via the branch build and PR’s terraform can be posted on the PR itself via GitHook from Jenkins slave to Git PR. Once approved promotion and apply parts can be done via the pipeline.
